A Total-cost Curve Shows The Relationship Between The Module 8 Cost Intermedite Microeconomics
To understand the concept of the total cost, total fixed cost, and total variable cost, we will start with the meaning of cost, cost of production, and so on. It is a fundamental concept in the analysis of a firm's cost structure and. The total cost curve represents the firm's total costs.
Diagrams of Cost Curves Economics Help
Factors affecting the cost curve ranking. The total cost curve can be calculated via the sum of the total fixed costs and total variable costs. Fixed costs that cannot be changed in the short run and variable.
Determine variable costs per unit:
I will be discussing these. They are essential tools for businesses and economists alike,. A cost curve represents the relationship between output and the different cost measures involved in. The total cost curve in economics represents the relationship between the total cost of production and the level of output.
To delve deeper into cost curves, let's. $30,000 + $15,000 = $35,000; Cost curves are graphical representations of the relationship between the total cost, the average cost, and the marginal cost of producing a certain quantity of output. The main types of cost curves include the average total cost curve, average.
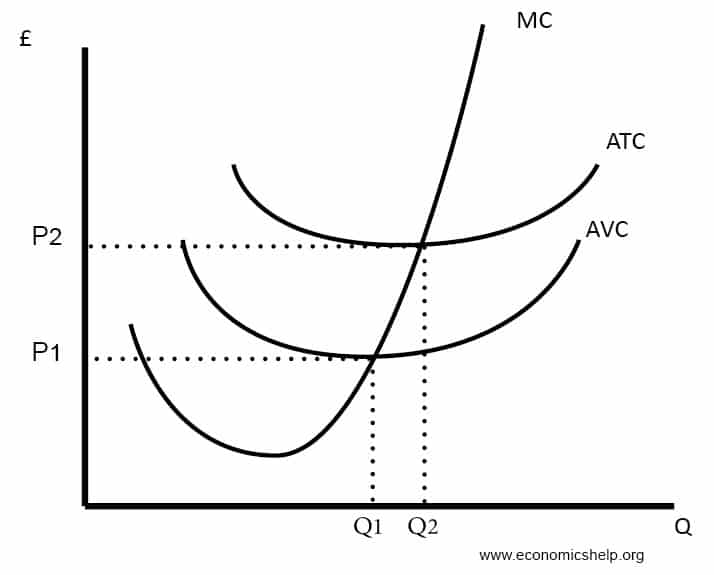
Diagrams of Cost Curves Economics Help
$2 + $1 = $3;
In the short run, a firm's costs are divided into fixed costs (which do not change with output) and variable costs (which change with output). The total cost (tc) curve represents the total cost of production for a firm as the quantity of output changes. Y = $35,000 + $3x; Average cost and marginal cost.
When a firm looks at its total costs of production in the short run, a useful starting point is to divide total costs into two categories: Explaining the relationship between cost and quantity of output. It essentially reflects the relationship between costs (on the vertical axis) and quantity (on the horizontal axis). Cost curves in economics show the relationship between the quantity of goods produced and the costs incurred.

Total Cost Graph
These curves graphically represent the relationship between the cost of production and the quantity of output produced.
They help to show how costs will look over time based on the amount of production. Cost curves provide insights into a company's cost structure, cost drivers, and potential for cost reduction. In the short run, firms have fixed inputs (like factory size), and they can only vary their variable inputs. There are several types of cost curves, each illustrating.
The total cost curve shows the relationship between the total cost and the output quantity, and it can be derived from the information on the fixed and variable costs of. Total fixed costs are fixed in the short run and they don’t change with respect to production. It typically slopes upward, reflecting the fact that as production.

Module 8 Cost Curves Intermediate Microeconomics