Are Vacuole In Prokaryotic Or Eukaryotic Cells Comparg And Prciples Of Biology
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: Vacuoles play many roles but. The central vacuole takes up most of the volume of the cell.
Diagram Of Prokaryotic Cell And Eukaryotic Cell Differences
Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane (figure \(\pageindex{2}\)) made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates. The vacuole is a vesicle, not an organism, but prokaryotic organisms might have vacuoles.
Vacuoles are present in just eukaryotic cells for the osmotic balance of their cells.
A large central vacuole is present in the plants that keep the cell turgid. [1][2] vacuoles are essentially enclosed. A vacuole is a characteristic organelle found in eukaryotic cells. The plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, plastids, and.
Almost all types of cells (bacterial, animal, plant, fungal, and protozoan cells) have a cell organelle called vacuoles. It is transparent, but you can see where it's pressing the chloroplasts up against the cell wall, especially at the ends of the cell. These figures show the major organelles and other cell components of (a) a typical animal cell and (b) a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Are vacuoles found in prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells?

Vacuole Main Function In Plant Cell
Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within.
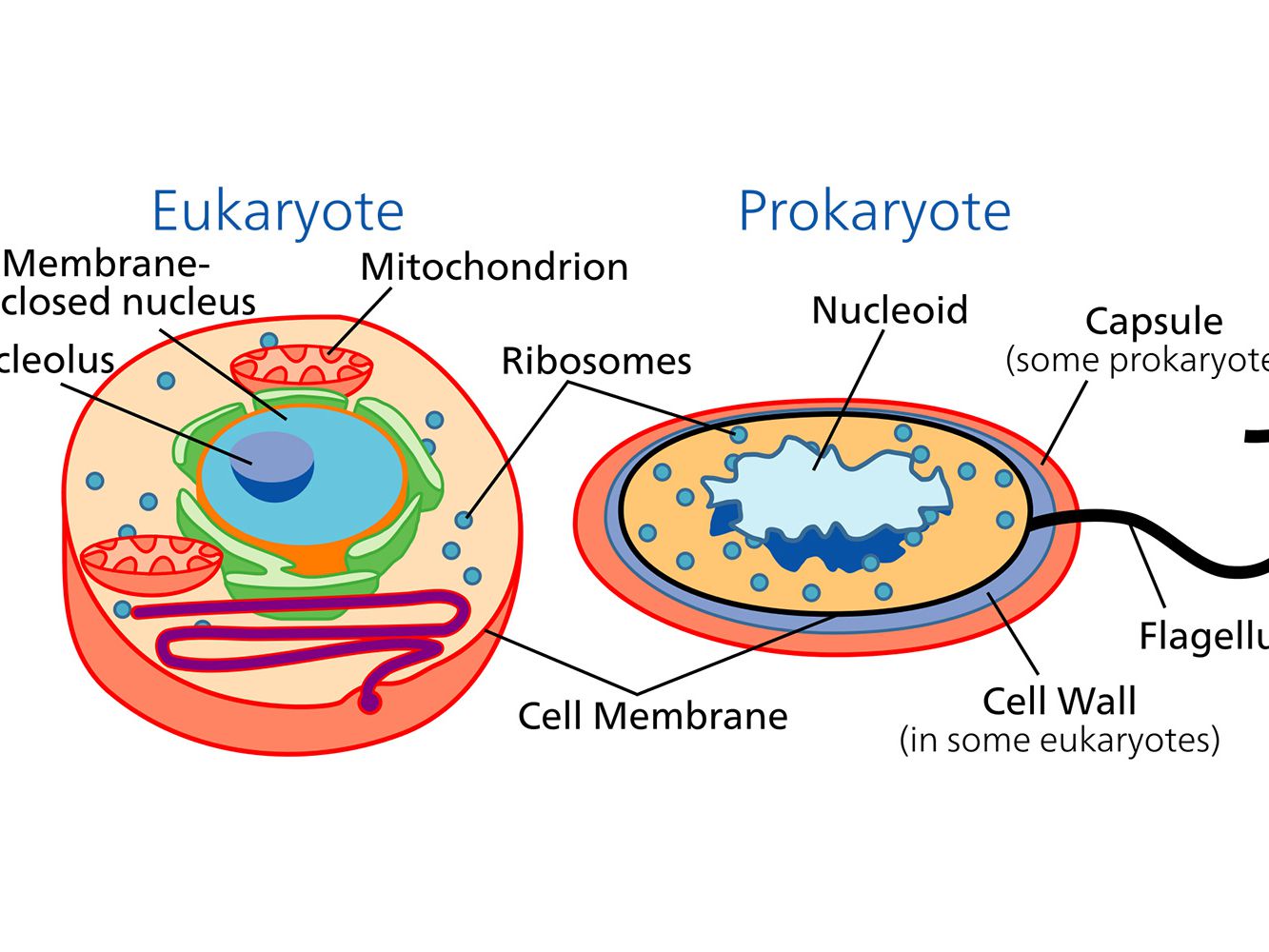
Diagram Of Prokaryotic Cell And Eukaryotic Cell Differences

Comparing Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells