Which Bond Is The Backbone Of All Protein Molecules Ppt Structure Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id6076024
Explain the role of the peptide backbone in the structure and stability of proteins. The bond that forms the backbone of all protein molecules is the peptide bond. Proteins are complex molecules that play a crucial role in various biological processes within.
Levels Of Protein Structure Diagram Structure Protein Levels
The peptide chain is known as the backbone, and the r groups are known as side chains. They are all, however, polymers of alpha amino acids, arranged in a linear sequence and connected together by covalent bonds. It participates in a series of.
The primary structure of proteins.
Protein secondary structure refers to the way the primary structure of a protein arranges itself as a result of regular hydrogen bonds forming between the backbone c = o and nh groups of each. 1 identify the type of bond that forms the primary structure of proteins. The term primary structure is used in. The structure of proteins is generally described as having four organizational levels.
It consists of a continuous chain of amino acid residues linked together. The protein backbone, also known as the peptide backbone, is the fundamental structural framework of proteins. Identify how peptide bonds, hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, van der waals forces, and the hydrophobic effect contribute to each level of protein architecture. The peptide backbone provides the structural framework for proteins, connecting the individual amino acid.
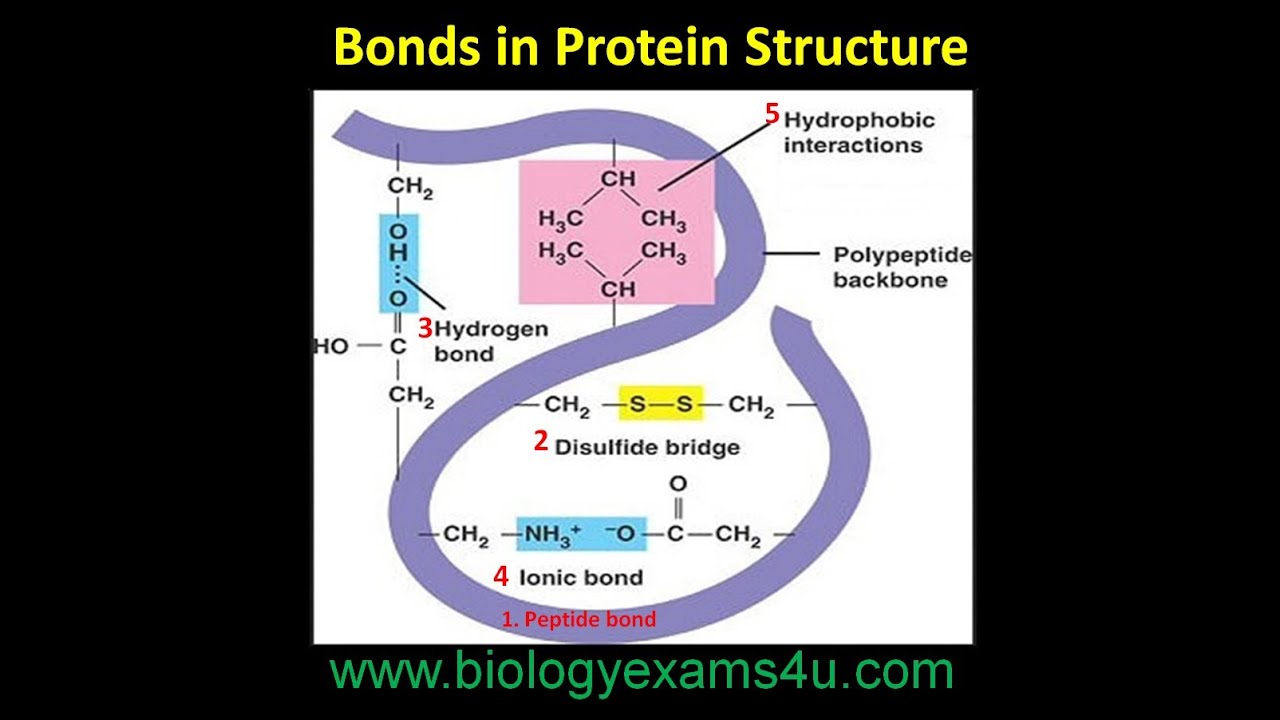
Bonds in Protein Structure Biomolecules Biochemistry
It is translated from rna and composed of amino acid connected by peptide bonds.
2 peptide bonds link amino acids together in a protein chain. These linkages have designated carbon atom positions of alpha, beta, and gamma, corresponding to specific positions relative to the peptide. These bonds form the backbone of proteins, connecting amino acids. All of the residues connect via peptide bonds.
The backbone of the protein can also become a helical structure (also a secondary structure) where the hydrogen bonds form between the different layers of the helix. The peptide chain is known as the backbone, and the r groups are known as side chains. This bond is formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of an. The major building block of proteins are called alpha.

Levels Of Protein Structure Diagram Structure Protein Levels
Protein is a major component of protoplasm, which is the basis of life.
The amide bonds have been formed by.

PPT Introducing proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID