Can A Hole Be A Absolute Maximum Or Minimum Solved 1 Point Find The Bsolute Mximum Nd
It says that if you look for an absolute max or. There is a relative maximum of \(f\) at \(x = c\) if \(f(c) \ge f(x)\) for all \(x\) near \(c\text{,}\) while there is an absolute maximum at \(c\) if \(f(c) \ge f(x)\) for all \(x\) in the domain of \(f\text{.}\) For all real numbers \ (x\), we say \ (f\) has an absolute maximum over \ ( (−∞,∞)\) at \ (x=0\).
Finding Absolute Maximum and Minimum Values Absolute Extrema YouTube
Look at figure 3(b) below. It can have both, one or the other, or neither. According to the definition in the red box of your second scanned image, the number $f(c)$ is.
A function may have both an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum, just one extremum,.
A function may have both an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum, just one extremum, or neither. Y 0 is the absolute maximum of f (x) on i if and only if y 0 >= f (x) for all x on i. No, there is not an absolute max at a hole in a mathematical function. B) the hole is always the absolute maximum.
We say that f (x) has an absolute (or global) maximum at x = c if f (x) ≤ f (c) for every x in the domain in which we're working. The absolute maximum is \ (f (0)=1\). At a hole, there is no. Thank you so much for an explanation.

Can a Straight Line Have Absolute Maximum Minimum YouTube
Also, a function that has a ‘break’ or ‘gap’ at a value of x may or may not have an absolute minimum or maximum.
There is an absolute minimum at x1, but there is no absolute maximum value, since the greatest function value goes toward infinity. When looking for the absolute maximum and minimum in a function, what happens if there is a hole at either location. Because the near $c$ language in the definition means near $c$ on both sides of $c$. A function cannot have a local max or min where it is not defined.
Ftfy, but your conclusion is still true: Maximum and minimum points must be endpoints or solutions of f0(x) = 0, namely 3x2 1 = 0, or x= p1 3 ˇ 0:58. Apparently $x=4$ is not a local maximum. (a) a function need not have an absolute max or absolute min.

Absolute minimum Definition, Conditions, and Examples
A hole in a function occurs when there is a removable discontinuity, which means that the function is undefined at that point but can be filled in to create a continuous function.
A hole is a point of discontinuity of at which the function is not defined, but at which a limit exists in every direction. When looking for the absolute maximum and minimum in a function, what happens if there is a hole at either location. Figure 2 shows several functions and some of the different possibilities regarding absolute extrema. The second observation is important:
The difference between a relative maximum and an absolute maximum: It occurs at \ (x=0\), as shown in figure (b). F(p1 3) ˇ1:4 <f(3 2) ˇ2:9, so. If we have a hole in the graph, we cannot use it as our absolute max, so wouldn't we take the next highest point in our domain?
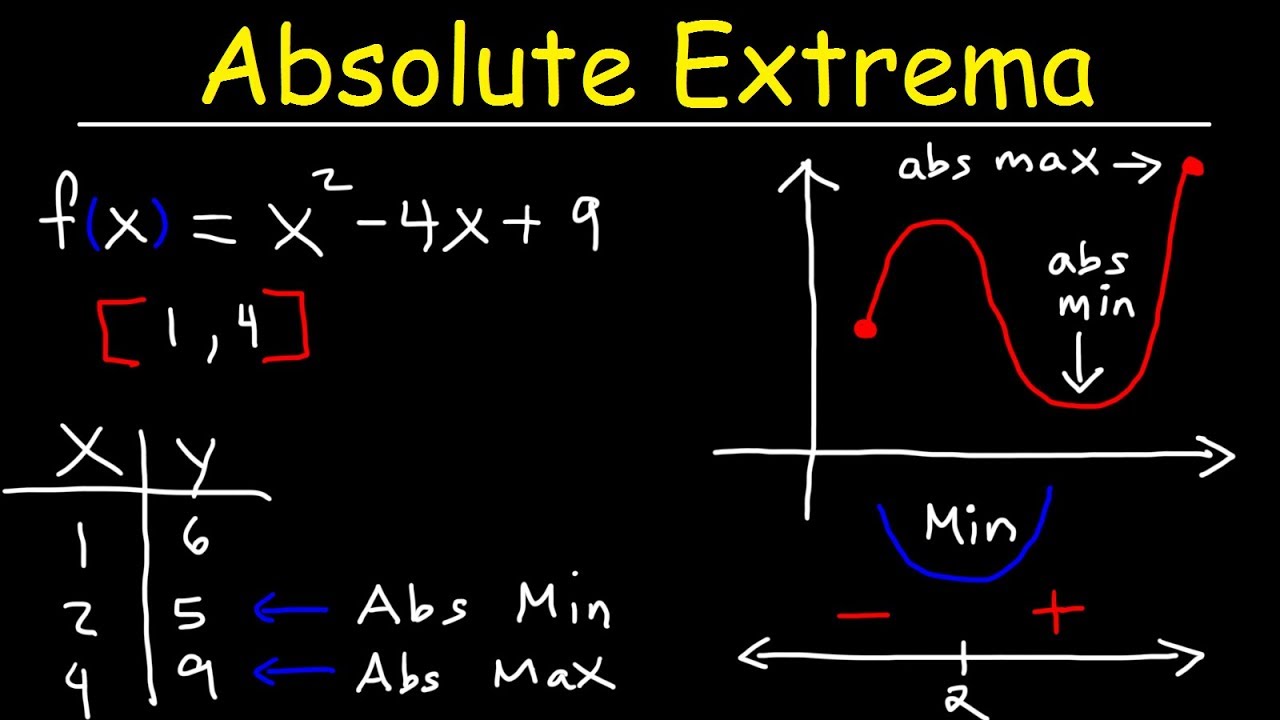
Finding Absolute Maximum and Minimum Values Absolute Extrema YouTube
A) the hole may be a candidate for the absolute maximum or minimum.
Y 0 is the absolute minimum of f (x) on i if and only if y 0 <= f (x) for all x on i. I was curious why there wouldn't be an absolute maximum at f(3). (b) a continuous function must have an absolute max and an absolute min on a closed interval. There is an absolute minimum at x1, but there is no absolute maximum value, since the greatest function value goes toward infinity.
We say that f (x) has an absolute (or global) minimum at x = c if f (x) ≥ f (c) for every x in the domain in which we're working.