Choose The Outcomes Of Microbial Metabolism. Solution Metabolism Lecture Part A Studypool
The bacterial metabolic state, host context and the drug mechanism of action collectively impact the bacterial response to antibiotics. Assembles smaller molecules into larger macromolecules needed for the cell; Learn how microbes harvest the chemical energy stored in nutrient molecules and use it to generate atp.
Microbial Metabolism SCIENTIST CINDY
Learn the definitions, terms, and concepts related to catabolism, anabolism, enzymes, atp, and more. Throughout earth’s history, microbial metabolism has been a driving force behind the development and maintenance of the planet’s biosphere. Decades of study have resulted in a solid understanding of.
Throughout earth’s history, microbial metabolism has been a driving force behind the development and maintenance of the planet’s biosphere.
Microbial metabolism normally transports electrons intracellularly from electron donors (e.g. Explore the processes of catabolism and anabolism, and the steps of aerobic. Gut microbes are crucial to the development of ibd and play a key role in regulating the host’s normal physiological functions and disease progression, establishing a dynamic and. In turn, antibiotics can directly alter the.
Eukaryotic organisms such as plants. Microbial metabolism is a complex system of interwoven pathways coordinated by an intricate, multilayered regulatory network. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the outcomes of microbial metabolism, regular use of ______ may cause constipation., body system in charge of. Test your knowledge of microbial metabolism with this set of flashcards.

PPT Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Organic compounds) to electron acceptors (e.g.
Prokaryotes can metabolize a wide. Microbial metabolism can fuel intestinal cells, synthesize vitamins, and aid in digestion, but an imbalance can lead to metabolic disorders. Throughout earth’s history, microbial metabolism has been a driving force behind the development and maintenance of the planet’s biosphere. Microbial metabolism is based on the principle of harnessing the energy flow during chemical transformation, typically by transporting nutrients into the cell, creating these gradients by.
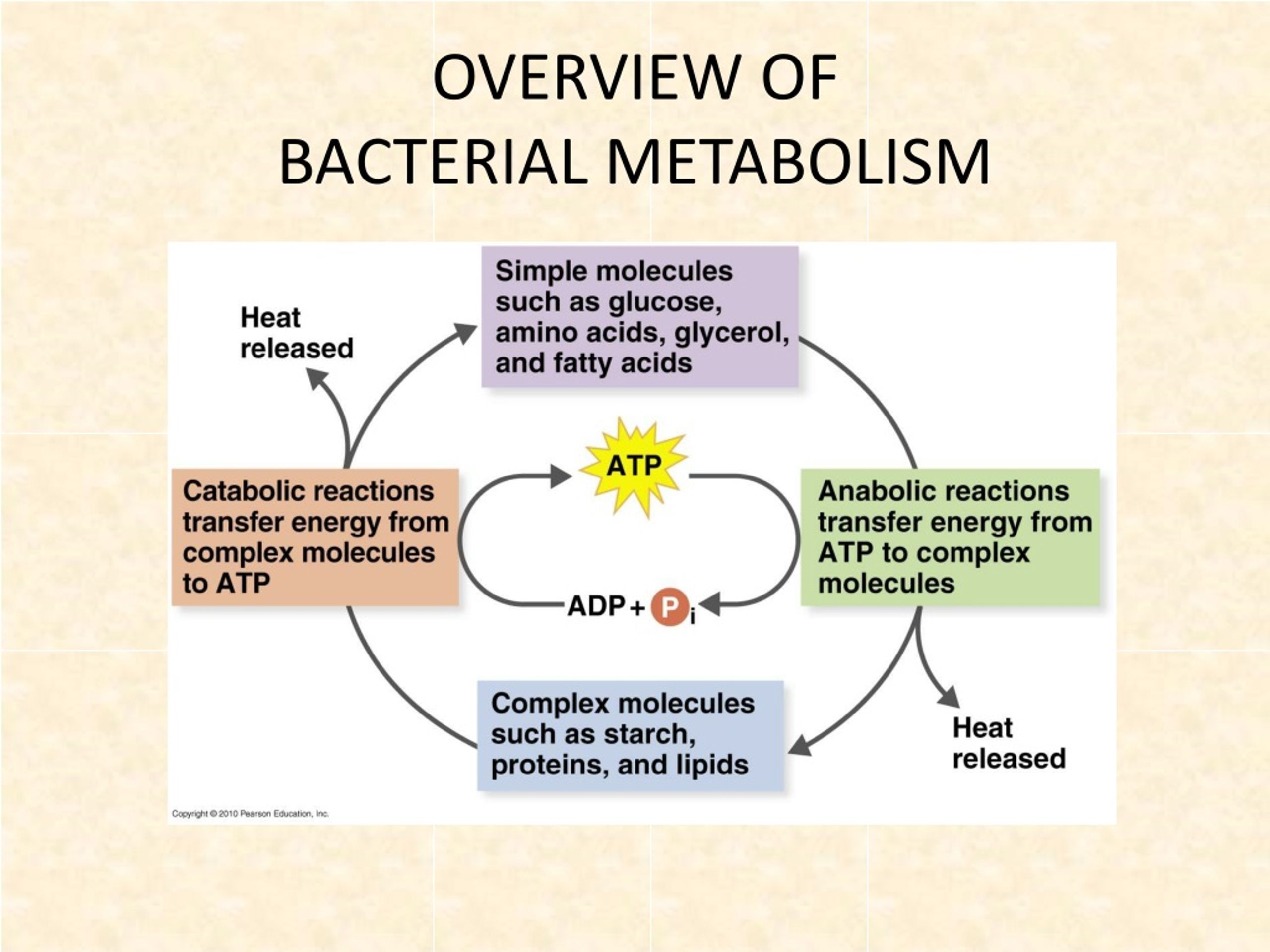
Microbes use many different types of metabolic. It binds to egr1, suppressing. In this process, atp is utilized to form bonds (anabolism) 2. Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients (e.g.
PPT MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309, 2012 Kim and Gadd, Chapter 4
Carbon) it needs to live and reproduce.
By studying the complete set of metabolites within a microorganism and monitoring the global outcome of interactions between its development processes and the environment,. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like out line the stages of metabolism that lead directly to the growth of microbial populations, being sure to include.

Microbial Metabolism SCIENTIST CINDY