How Does Fluoroquinolones Affect And Destroy Bacteria Dna Topoisomerase Targets Of The A Strategy For
Classification, occurrence, and ecotoxicological effects of fq have been discussed. The fluoroquinolones are the only direct inhibitors of dna synthesis; Fluoroquinolone drugs are active against a wide range of gram‐negative and gram‐positive pathogens and show improved oral absorption and systemic distribution.
NeuroSci Free FullText FluoroquinolonesAssociated Disability It
Fluoroquinolones also differ in the extent to which common bacterial multidrug efflux pumps affect their activity, with some compounds being unaffected by resistance mechanisms. Ciprofloxacin is the most active against pseudomonas aeruginosa. The newer fluoroquinolones are a major advance in antimicrobial chemotherapy.
The bacterial metabolic state, host context and the drug mechanism of action collectively impact the bacterial response to antibiotics.
Early generation fluoroquinolones hamper bacterial dna synthesis during replication primarily by inhibiting dna gyrase, one enzyme required for bacterial (but not human) dna. Quinolones trap topoisomerases on dna in reversible complexes that block dna replication and bacterial growth. Since the first quinolone nalidixic acid was developed, the quinolones have undergone structural modifications, in particular the addition of a fluorine at position 6, to produce the. Fluoroquinolones act by inhibiting two enzymes involved in bacterial dna synthesis, both of which are dna topoisomerases that human cells lack and that are essential for.
Antimicrobial prescriptions for the treatment of infections caused in particular by staphylococcus aureus (s. In turn, antibiotics can directly alter the. One of the key biomechanisms that affects the environmental effect of fluoroquinolones is their interaction with microorganisms. They inhibit the supercoiling activity of the dna gyrase enzyme, thus exerting their antibacterial action on dna.
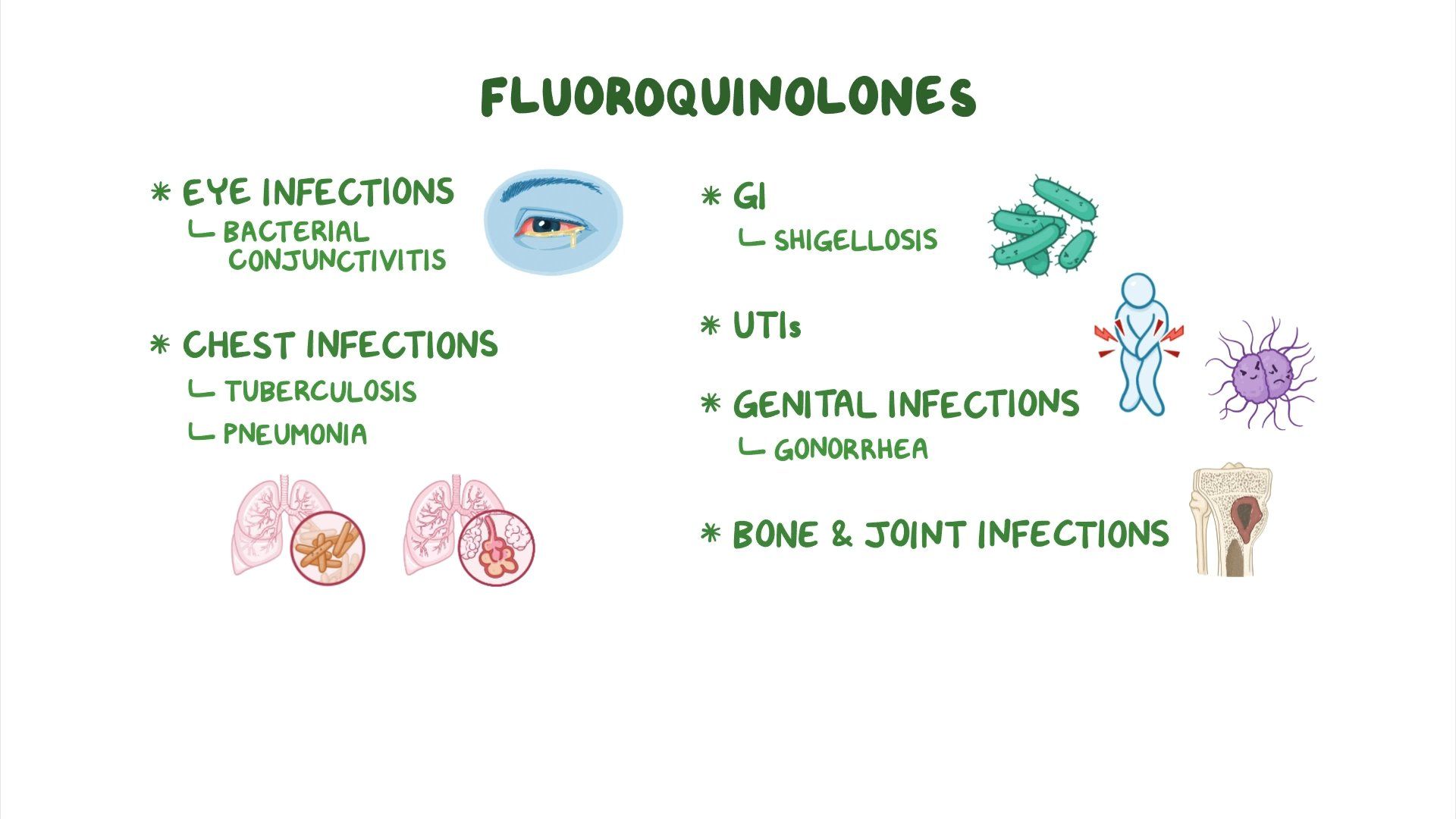
Antibiotics Fluoroquinolones Osmosis Video Library
At elevated drug concentrations, dna ends are released from.
As an antimicrobial class, the fluoroquinolones exert antimicrobial activity by direct inhibition of dna synthesis due to interaction between the fluoroquinolone and two enzymes. The fluoroquinolones are a family of broad spectrum, systemic antibacterial agents that have been used widely as therapy of respiratory and urinary tract infections.

Mechanisms of Antibacterial Drugs · Microbiology

NeuroSci Free FullText FluoroquinolonesAssociated Disability It